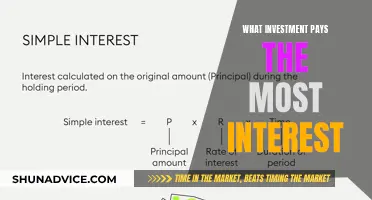
Interest rate fluctuations have a substantial effect on the stock market, inflation, and the economy as a whole. When interest rates are high, businesses may borrow and invest less due to higher lending costs and potentially stop hiring, which may reduce consumer spending as incomes fall. However, when interest rates are low, consumers are encouraged to spend more, and businesses are encouraged to expand and produce more goods, creating new jobs.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Effect on the stock market | Higher interest rates mean cutbacks in spending for stock investors |
| Effect on inflation | Raising interest rates can combat inflation |
| Effect on the economy | Higher interest rates can calm the economy |
| Effect on businesses | Higher interest rates may cause businesses to borrow and invest less due to higher lending costs |
| Effect on consumer spending | Higher interest rates may reduce consumer spending as incomes fall |
What You'll Learn

Higher interest rates and the stock market
Interest rate fluctuations have a substantial effect on the stock market, inflation, and the economy as a whole. When interest rates are high, businesses may borrow and invest less due to higher lending costs. This can lead to cutbacks in spending and potentially stop hiring, which may reduce consumer spending as incomes fall.
For stock investors, higher interest rates mean cutbacks in spending. This is because higher interest rates increase the cost of borrowing for businesses, making it more expensive to invest in new projects or expand operations. As a result, businesses may choose to reduce their spending on stock purchases or other investments to maintain their profitability.
On the other hand, lower interest rates encourage big purchases by consumers and expansion by businesses. Lower interest rates make it cheaper for businesses to borrow money, which can lead to increased production and the creation of new jobs. This, in turn, can stimulate the economy and drive corporate profits.
The Federal Reserve's decision to change interest rates has a ripple effect throughout the broader economy, affecting both stock and bond markets in different ways. When the Fed increases interest rates, it can combat inflation and calm the economy. However, it may also lead to reduced investment spending and slower economic growth. Therefore, the Fed must carefully consider the potential impact on investment spending when making decisions about interest rates.
Foreign Investments: Interest Rates and Their Intricate Relationship
You may want to see also

Higher interest rates and inflation
Interest rate fluctuations have a substantial effect on the stock market, inflation, and the economy as a whole. When the economy is growing too fast, the Fed may increase interest rates slightly to keep inflation at bay. Raising interest rates can combat inflation and calm the economy. When the economy is growing quickly, the Fed may become concerned about inflation or other issues of too-fast economic growth. In this case, the Fed can pump the brakes and increase the target federal funds rate.
With higher interest rates, businesses may borrow and invest less due to higher lending costs and potentially stop hiring, which may reduce consumer spending as incomes fall. For stock investors, higher interest rates mean cutbacks in spending. Meanwhile, lower interest rates encourage big purchases by consumers and expansion by businesses. These changes feed back into corporate profits, for better or worse.
For bond investors, higher interest rates mean higher rates on new bond issues but a decline in the values of existing bonds. Lower interest rates have the opposite effects; new bond issues offer less interest while existing bonds trade at a premium. Understanding the relationship between interest rates and markets can help investors make better financial decisions.
Lowering interest rates is the Fed's most powerful tool to increase investment spending in the U.S. and to attempt to steer the country clear of recessions. If economic growth is lagging and unemployment is rising, the Fed can lower interest rates to make it cheaper to borrow money. During an economic downturn, the Fed may lower interest rates to encourage additional investment spending.
Retirement Investment Interest Rates: What's the Average?
You may want to see also

Higher interest rates and the economy
Higher interest rates can have a significant impact on the economy. When the economy is growing too fast, the Fed may increase interest rates to keep inflation at bay. Raising interest rates can combat inflation and calm the economy.
When interest rates are higher, businesses may borrow and invest less due to higher lending costs. This could potentially cause businesses to stop hiring new employees, which may reduce consumer spending as incomes fall.
For stock investors, higher interest rates mean cutbacks in spending. However, for bond investors, higher interest rates mean higher rates on new bond issues but a decline in the value of existing bonds.
Lower interest rates, on the other hand, can stimulate the economy. If economic growth is lagging and unemployment is rising, the Fed can lower interest rates to make it cheaper to borrow money. Lower interest rates for consumers mean more spending, while lower interest rates for businesses mean increased production of goods and the creation of new jobs.
The Magic of Compounding: How Interest Grows Investments
You may want to see also

Higher interest rates and consumer spending
Higher interest rates can reduce investment spending because they increase the cost of borrowing money. This means that businesses may borrow and invest less, and may also stop hiring new employees. This can lead to a reduction in consumer spending as incomes fall.
When interest rates are high, consumers are more likely to save their money in savings accounts or certificates of deposit, rather than spending it. This can further slow down the economy.
The Federal Reserve (Fed) uses monetary policy to keep the economy stable. During an economic downturn, the Fed may lower interest rates to encourage additional investment spending. Lower interest rates make it cheaper for businesses to borrow money, which can lead to increased production and the creation of new jobs. This, in turn, can increase consumer spending as people have more money to spend.
For stock investors, higher interest rates mean cutbacks in spending. Lower interest rates encourage big purchases by consumers and expansion by businesses, which can feed back into corporate profits.
Private Equity Investing: Your Interests and Strategies
You may want to see also

Higher interest rates and business spending
Higher interest rates can reduce business spending in a number of ways. Firstly, they can make borrowing more expensive, which may cause businesses to borrow less. This can lead to reduced investment spending as businesses have less money to invest.
Secondly, higher interest rates can cause incomes to fall, which may lead to reduced consumer spending. This, in turn, can cause businesses to reduce their spending as they may not need to produce as many goods or services.
Thirdly, higher interest rates can affect the stock market, which can impact business spending. When interest rates rise, stock investors tend to cut back on spending, which can affect corporate profits.
Finally, higher interest rates can also impact the bond market. While higher interest rates mean higher rates on new bond issues, they also cause a decline in the value of existing bonds. This can affect business spending as businesses may hold bonds as part of their investment portfolio.
Overall, while higher interest rates can help combat inflation and stabilise the economy, they can also lead to reduced business spending through a variety of channels.
Structuring Simple Interest Investment Deals: A Comprehensive Guide
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Higher interest rates can reduce investment spending because they increase lending costs, which means businesses may borrow and invest less.
The federal funds rate is the shortest of short-term interest rates. When the Fed increases the federal funds rate, it indirectly adjusts long-term interest rates, which do affect investment spending.
The Fed uses monetary policy to keep the economy stable. It can lower interest rates to increase investment spending and steer the country clear of recessions, or it can increase interest rates to keep inflation at bay.