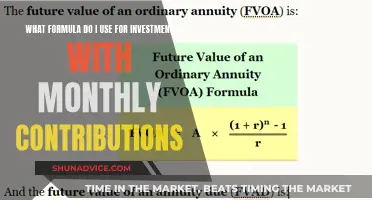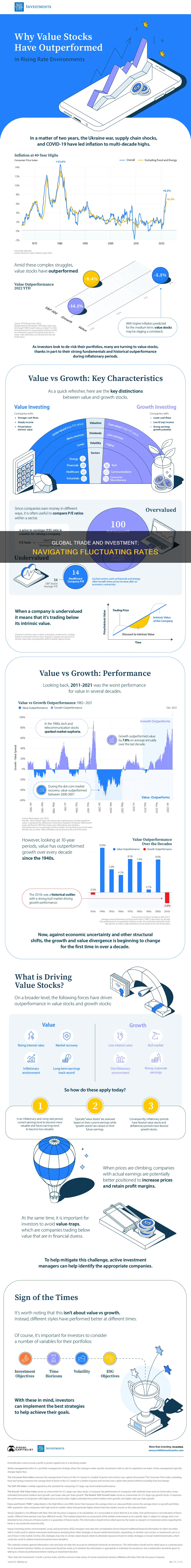
The interplay between investments, foreign trade rates, and economic growth is a complex and multifaceted topic. Understanding how these factors influence each other is crucial for policymakers, investors, and businesses alike. In this paragraph, we will explore the potential effects of investments and foreign trade rates on economic performance. By examining historical trends and theoretical frameworks, we can gain insights into how these variables interact and how they might impact a country's economic development.
What You'll Learn
- Impact of Interest Rates: Higher interest rates may attract foreign investment, boosting trade and increasing rates
- Exchange Rate Fluctuations: Volatile exchange rates can impact investment decisions, affecting trade and rates
- Government Policies: Trade policies and investment incentives can influence foreign trade and exchange rates
- Economic Growth: Strong economic growth can increase investment and trade, impacting exchange rates
- Market Sentiment: Positive market sentiment may encourage investment and trade, potentially affecting foreign exchange rates

Impact of Interest Rates: Higher interest rates may attract foreign investment, boosting trade and increasing rates
The relationship between interest rates and foreign investment is a critical aspect of a country's economic landscape. When a country's central bank raises interest rates, it has a significant impact on the flow of capital in and out of the country. Higher interest rates can indeed attract foreign investment, which can have a positive ripple effect on the economy.
As interest rates rise, foreign investors become more interested in the country's financial markets. This is because higher rates offer a more attractive return on investment compared to their home countries or other international markets. Foreign investors seek opportunities to maximize their returns, and when a country's interest rates are elevated, it becomes an appealing destination for their capital. This influx of foreign investment can lead to increased demand for the country's currency, causing its value to appreciate. A stronger currency can make the country's exports more expensive, potentially reducing their competitiveness in international markets. However, it can also make imports cheaper, which may stimulate domestic consumption and benefit certain industries.
The impact of higher interest rates on foreign investment is twofold. Firstly, it encourages the flow of capital into the country, providing a boost to the financial sector and potentially increasing the overall wealth of the nation. Secondly, it can lead to a surge in foreign direct investment (FDI), where investors establish businesses or acquire assets in the country. This FDI can drive economic growth, create jobs, and contribute to the development of local industries. As a result, the country's trade balance may improve, with exports and imports both increasing, but potentially at a more balanced rate.
The effects of higher interest rates on trade are also noteworthy. With increased foreign investment, the country's trade partners may become more interested in doing business with it. This can lead to a surge in exports as foreign buyers seek to purchase goods and services from the country. Additionally, the appreciation of the domestic currency can make imports more affordable, encouraging consumers to purchase foreign products. This dynamic can create a more diverse and robust trade environment, reducing the country's reliance on a few key trading partners.
In summary, higher interest rates can have a positive impact on a country's economy by attracting foreign investment and stimulating trade. The increased investment can lead to economic growth, job creation, and a more robust financial sector. However, it is essential to monitor the effects on the trade balance and ensure that the benefits of higher interest rates are not offset by potential drawbacks, such as reduced export competitiveness or increased import costs. A well-managed monetary policy, considering both the domestic and international economic landscape, is crucial for harnessing the full potential of higher interest rates.
Strategies for Investing Uninvested Cash in a VA529 Plan
You may want to see also

Exchange Rate Fluctuations: Volatile exchange rates can impact investment decisions, affecting trade and rates
Volatile exchange rates can significantly influence investment strategies and international trade, often leading to a complex interplay of effects. When exchange rates fluctuate, the value of a country's currency relative to others changes, which can have both positive and negative consequences for investors and traders. This dynamic environment presents both opportunities and challenges, requiring careful consideration and analysis.
For investors, volatile exchange rates can impact their decision-making processes. On one hand, a weakening domestic currency can make foreign investments more attractive as the returns from these investments will be worth more in the local currency. This can encourage investors to seek opportunities abroad, potentially increasing foreign direct investment (FDI). For instance, a U.S. investor might find it advantageous to invest in a European startup when the euro is strong against the dollar, as the profits will be more substantial upon conversion back to U.S. currency. Conversely, a strengthening currency could make domestic investments more appealing, as the returns will be worth more in local currency terms. This dynamic can lead to shifts in investment portfolios, with investors rebalancing their holdings to take advantage of favorable exchange rate conditions.
In the context of international trade, exchange rate volatility can have a substantial impact on a country's exports and imports. A country with a depreciating currency may experience an increase in exports as its goods become relatively cheaper for foreign buyers. This can boost the country's trade balance and stimulate economic growth. For example, a country with a rapidly falling currency might see a surge in demand for its agricultural products, leading to increased exports and revenue. However, a strengthening currency can have the opposite effect, making imports cheaper and potentially leading to a trade deficit. This scenario can be particularly challenging for industries that heavily rely on imports, such as the automotive sector, as the cost of raw materials and components may rise, impacting production and profitability.
The relationship between exchange rates and trade is bidirectional. As trade increases, it can lead to a higher demand for the country's currency, causing it to appreciate. This appreciation can then make the country's exports more expensive on the international market, potentially reducing their competitiveness. On the other hand, a weaker currency can stimulate exports by making the country's goods more affordable for foreign buyers, thus increasing trade volumes. This complex interplay between exchange rates and trade can create a feedback loop, where changes in one area can have a ripple effect on the other.
In summary, volatile exchange rates can serve as a double-edged sword for investments and foreign trade. While they may present opportunities for investors to capitalize on favorable exchange rate movements, they can also introduce challenges and uncertainties. For policymakers and businesses, understanding these dynamics is crucial for making informed decisions, whether it's adjusting investment strategies, managing trade risks, or implementing policies to stabilize the economy during periods of high exchange rate volatility. Effective management of exchange rate fluctuations is essential to ensure a country's economic stability and growth in an increasingly interconnected global market.
Computing Net Proceeds: Investing Cash Flow Explained
You may want to see also

Government Policies: Trade policies and investment incentives can influence foreign trade and exchange rates
Government policies play a crucial role in shaping the dynamics of foreign trade and exchange rates. Trade policies, such as tariffs, quotas, and subsidies, directly impact the cost and availability of imported and exported goods, which in turn affects the demand and supply of a country's currency in the foreign exchange market. For instance, a government may impose a tariff on imported goods to protect domestic industries, making those goods more expensive for foreign buyers. This can lead to a decrease in imports and potentially increase the demand for the domestic currency, causing its value to appreciate against other currencies. Conversely, if a government reduces tariffs or implements trade liberalization measures, it can stimulate foreign trade, increase imports, and put downward pressure on the domestic currency, leading to depreciation.
Investment incentives are another powerful tool in a government's arsenal to influence foreign trade and exchange rates. These incentives can take various forms, such as tax breaks, subsidies, and special economic zones. By offering these incentives, governments aim to attract foreign direct investment (FDI) and promote the establishment of businesses within their borders. FDI often brings capital inflows, which can strengthen the domestic currency as foreign investors convert their funds into the local currency. Additionally, increased investment can lead to higher production and exports, further impacting the exchange rate. For example, a country offering generous tax incentives for manufacturing industries might attract foreign investors, resulting in a surge of foreign investment and a subsequent increase in the value of its currency.
The effectiveness of these policies is often context-specific and depends on various factors, including the country's economic structure, the global economic environment, and the specific goals of the government's policy framework. In some cases, governments may use a combination of trade and investment policies to achieve multiple objectives. For instance, a country might implement trade restrictions to protect nascent industries while simultaneously offering investment incentives to attract foreign companies, aiming to boost both domestic production and foreign investment. Such a strategy can have complex effects on foreign trade and exchange rates, requiring careful consideration and analysis.
In summary, government policies, particularly trade policies and investment incentives, have a significant impact on foreign trade and exchange rates. These policies can either stimulate or restrict international trade, influence the demand for a country's currency, and ultimately determine the strength or weakness of its exchange rate. Understanding these relationships is essential for policymakers, businesses, and investors alike, as it enables them to make informed decisions and navigate the complexities of the global economy.
Strategizing Initial Investment: Deciding Your First Cash Flow
You may want to see also

Economic Growth: Strong economic growth can increase investment and trade, impacting exchange rates
Strong economic growth is a powerful catalyst for increased investment and foreign trade, which in turn can significantly influence exchange rates. When an economy is thriving, it often attracts domestic and foreign investors alike, as the potential for higher returns and a more stable environment becomes apparent. This surge in investment can lead to a variety of positive outcomes, including the expansion of businesses, the creation of new jobs, and the overall strengthening of the economy. As a result, the demand for the country's currency increases, as investors and traders seek to purchase goods and services denominated in that currency. This heightened demand can cause the exchange rate to appreciate, making the country's currency more valuable relative to others.
The relationship between economic growth and foreign trade is equally important. A robust economy often leads to a higher demand for imports, as consumers and businesses have more purchasing power. This increased demand can drive up the prices of imported goods and services, making them more expensive in the domestic market. Consequently, foreign traders and investors may seek to convert their foreign currencies into the country's currency to take advantage of these higher-priced imports. This increased demand for the domestic currency can further contribute to its appreciation in value.
Moreover, strong economic growth can lead to a positive feedback loop in the investment and trade sectors. As investment increases, businesses may expand their operations, leading to higher production and potentially more exports. This, in turn, can attract even more foreign investment, as the country's economic prospects become more attractive. The cycle continues, with increased trade and investment further boosting economic growth and potentially impacting exchange rates.
However, it is essential to consider that the relationship between economic growth, investment, and exchange rates is complex and can be influenced by various factors. Other economic indicators, such as inflation, interest rates, and political stability, also play a significant role in determining exchange rates. For instance, if a country experiences high inflation while its trading partners' inflation rates are lower, the country's currency may depreciate despite strong economic growth.
In summary, strong economic growth has the potential to create a positive environment for increased investment and foreign trade, which can, in turn, impact exchange rates. The appreciation of a country's currency can be a result of heightened demand from investors and traders seeking to participate in the country's economic success. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for investors, traders, and policymakers, as it highlights the interconnectedness of economic growth, investment, and exchange rate movements.
Foreign Investment: A Double-Edged Sword for Nations
You may want to see also

Market Sentiment: Positive market sentiment may encourage investment and trade, potentially affecting foreign exchange rates
Positive market sentiment can significantly influence global economic activities, including investment flows and foreign trade, which in turn can have a notable impact on foreign exchange rates. When market sentiment is optimistic, it often leads to a surge in investor confidence, creating a favorable environment for both domestic and international business activities. This positive outlook can drive up the demand for a country's currency, as investors and traders anticipate growth and stability.
In the context of investments, positive market sentiment can attract foreign direct investment (FDI) and portfolio investment. Investors are more inclined to invest in a country when they perceive the market as promising, leading to an increase in capital inflows. This influx of investment can strengthen a country's currency, as the demand for the local currency rises to facilitate transactions. For instance, if Country A experiences a positive market sentiment due to favorable economic policies and strong growth prospects, investors might flock to invest in its stock market, real estate, or local businesses. This increased investment activity can lead to a higher demand for the country's currency, causing its value to appreciate against other currencies.
Similarly, positive market sentiment can boost international trade. When businesses and traders anticipate a prosperous future, they are more likely to engage in cross-border transactions. This heightened trade activity can result in a higher demand for the currencies of the trading partners, especially if the sentiment is widespread and sustained over time. For example, if Country B has a positive market sentiment due to successful trade negotiations and a strong economic outlook, its exports might become more attractive to foreign buyers. This could lead to an increase in the demand for Country B's currency, making it more valuable in the foreign exchange market.
The relationship between market sentiment and foreign exchange rates is intricate. While positive sentiment can drive up currency demand, it is essential to consider other economic factors as well. Central bank policies, interest rates, geopolitical events, and global economic trends also play significant roles in determining exchange rates. However, market sentiment often acts as a catalyst, influencing the direction and magnitude of these other factors. Therefore, monitoring market sentiment, along with other economic indicators, is crucial for investors, traders, and policymakers to make informed decisions and manage risks effectively.
In summary, positive market sentiment can be a powerful force in driving investments and international trade, which, in turn, can impact foreign exchange rates. Understanding and analyzing market sentiment, along with its interplay with other economic factors, is essential for navigating the complex world of global finance and making strategic choices in the realm of international trade and investment.
Maximizing Investment Earnings: Strategies for Optimal Utilization
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Investments and foreign trade rates can significantly impact a country's economy. When a country attracts more foreign investments, it can lead to increased capital inflow, which may strengthen the local currency and make exports more expensive, potentially decreasing foreign trade. However, it can also bring in new technologies, skills, and knowledge, boosting productivity and economic growth.
Interest rates play a crucial role in foreign trade. Higher interest rates in a country can attract foreign investors seeking higher returns, leading to increased foreign investments and a stronger local currency. This can make imports cheaper and exports more expensive, potentially impacting the trade balance. Conversely, lower interest rates might encourage exports by making them more competitive in the global market.
Exchange rate fluctuations can have a direct impact on international trade. A stronger domestic currency can make exports more expensive for foreign buyers, potentially reducing the volume of trade. On the other hand, a weaker currency can make imports more costly, encouraging local production and potentially increasing trade surplus. Exchange rate volatility can also deter investors, affecting the flow of foreign investments.