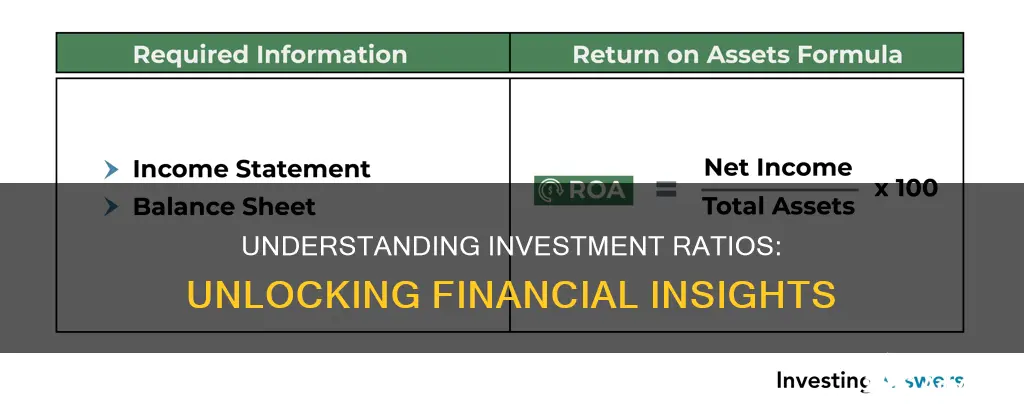
Investment ratios are a type of performance ratio that expresses profit as a percentage of the amount invested in a business. They are used to evaluate the return on capital employed or operating assets within a company. Investment ratios are used by investors to determine whether an initial or ongoing investment in a company is worthwhile. They can also be used to compare companies as potential investment opportunities.
There are several types of investment ratios, including:
- Earnings per share (EPS)
- Price-to-earnings ratio (P/E)
- Return on equity (ROE)
- Debt-to-capital ratio
- Interest coverage ratio
- Dividend yield ratio
- Dividend cover
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Purpose | Evaluating the return on capital employed or operating assets within the company |
| Formula | Profit as a percentage of the amount invested in a business |
| Examples | Return on capital employed, gross profit margin, stock turnover, debtor ratio, creditor ratio, liquidity ratio, gearing ratio, interest cover, gross dividend yield, gross percentage dividend, dividend cover, earnings per share, price-earnings ratio |
What You'll Learn

Return on capital employed
ROCE is an important metric for investors as it reflects the company's ability to generate returns on their investment. A high ROCE indicates that the company is generating attractive returns, which can instill confidence in investors and potentially attract more capital. It also helps assess the effectiveness of capital allocation decisions and the ability to generate returns on invested capital.
When comparing ROCE among companies, it is important to ensure that the companies are in the same industry, as comparisons across different industries may not offer much value. Additionally, it is important to compare ROCE figures for the same accounting period to avoid any misleading interpretations.
While a high ROCE generally indicates stronger profitability, it is important to consider other profitability ratios such as return on assets, return on invested capital, and return on equity to gain a comprehensive understanding of a company's financial performance.
ROCE can be particularly useful when comparing the performance of companies in capital-intensive sectors, such as utilities and telecoms, as it considers both debt and equity in its calculation.
Beat Financial Engines with Fidelity Investments Strategies
You may want to see also

Gross profit margin
The gross profit margin is the profit remaining after subtracting the cost of goods sold (COGS). It is calculated as net sales minus the COGS, divided by net sales.
Analysts use this metric to compare a company's business model with its competitors. Business owners can use it to identify areas for cost-cutting and sales improvement. A high gross profit margin indicates efficient operations, while a low margin suggests areas that need improvement.
For example, a company with a higher gross margin may have a competitive edge in the market due to reduced costs. On the other hand, a company with a low gross margin may need to increase prices to boost revenue, but this strategy could backfire if it leads to reduced sales.
A company's gross profit margin can be influenced by various factors, such as product pricing adjustments, operational changes, and external factors like market trends, interest rates, and economic conditions.
It is important to note that gross profit margin should be compared between companies within the same industry, as companies in the same industry generally have similar asset utilisation efficiency. A high gross profit margin indicates a more profitable and efficient company, but comparing margins within the same industry provides a fair assessment.
Using Debt to Leverage Investments: A Strategic Guide
You may want to see also

Stock turnover
Investment ratios are performance ratios that express profit as a percentage of the amount invested in a business. They are used to evaluate the return on capital employed or operating assets within a company.
The stock turnover ratio, also known as the inventory turnover ratio, is a financial ratio that shows how many times a company turned over its stock or inventory in a given period. It is calculated by dividing the net sales by all stockholders' equity and outstanding debt. A high stock turnover ratio indicates that a business can efficiently generate large sales volumes from a modest investment.
The stock turnover ratio is particularly important for retailers as it helps them make better decisions on pricing, manufacturing, marketing, and purchasing. It also allows them to assess whether they have sufficient inventory to support strong sales or whether they need to scale down due to lagging business.
However, it is important to note that the stock turnover ratio has some limitations. It is not related to profit, as a company may be generating sales but also incurring excessive expenses. Additionally, it may not be useful for comparing businesses in different industries, as the required investment levels can vary significantly.
A company has net sales of $2,000,000, stockholders' equity of $700,000, and long-term debt of $300,000.
The formula for the stock turnover ratio is:
Plugging in the values, we get:
This means that for every dollar invested, the company generates two dollars in sales.
In summary, the stock turnover ratio is a valuable metric for businesses, especially in the retail industry, as it helps them understand their efficiency in managing inventory and generating sales. However, it should be interpreted alongside other financial ratios and industry benchmarks to gain a comprehensive understanding of a company's financial health and performance.
Understanding Investment Cash Flow Entries and Their Impact
You may want to see also

Debtor ratio
Investment ratios are performance ratios that express profit as a percentage of the amount invested in a business. They are used to evaluate the return on capital employed or operating assets within a company.
The debtor ratio is one such investment ratio. It expresses debtors as a percentage of annual sales, multiplied by 365 to indicate how many days' sales have yet to be converted into cash.
A very small increase in debtor days can have a significant adverse impact on the company's cash flow. Therefore, a realistic target should be set for debtor days, and actual performance should be monitored closely against this.
The debtor ratio is calculated by dividing total liabilities by total assets, with higher ratios indicating higher degrees of debt financing. Debt ratios vary greatly among industries, so comparisons should be made within the same industry.
For example, capital-intensive businesses, such as manufacturing or utilities, can get away with slightly higher debt ratios when expanding their operations. On the other hand, businesses that are more cyclical should rely less on debt financing to avoid potential defaults during economic downturns when revenues and profits tend to be lower.
Investors usually look for a company to have a debt ratio between 0.3 (30%) and 0.6 (60%). From a pure risk perspective, debt ratios of 0.4 (40%) or lower are considered better, while a debt ratio of 0.6 (60%) or higher makes it more difficult to borrow money.
A company can improve its debt ratio by cutting costs, increasing revenues, refinancing its debt at lower interest rates, improving cash flows, increasing equity financing, and restructuring.
Salesforce Superpowers for Investment Firms: Strategies Unveiled
You may want to see also

Creditor ratio
Investment ratios are performance ratios that express profit as a percentage of the amount invested in a business. They are used to evaluate the return on capital employed or operating assets within a company.
The creditor ratio is one of the coverage ratios that measure the coverage that income, cash, or assets provide for debt or interest expenses. The higher the coverage ratio, the greater the ability of a company to meet its financial obligations.
The creditor ratio is also known as the accounts payable turnover ratio. It is a short-term liquidity measure used to quantify the rate at which a company pays off its suppliers. It shows how many times a company pays off its accounts payable during a particular period.
The ratio is calculated by dividing total supplier purchases for the period by the average accounts payable for the period. The average accounts payable for the period is calculated by adding the accounts payable balance at the beginning of the period to the balance at the end of the period and dividing the result by two.
A decreasing creditor ratio indicates that a company is taking longer to pay off its suppliers than in previous periods, which could signal financial distress. On the other hand, an increasing ratio means that the company is paying off suppliers at a faster rate, indicating effective debt and cash flow management.
However, an increasing ratio over a long period could also indicate that the company is not reinvesting money back into its business, which could result in a lower growth rate and lower earnings in the long term. Therefore, the ideal creditor ratio should allow a company to pay off its debts quickly and reinvest money in its business to promote growth.
The creditor ratio is listed on the balance sheet under current liabilities.
Cash Flows: Luring Investors with Predictable Returns
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
An investment ratio is a performance ratio that expresses the relationship between an amount of money invested and the profit made from it. It helps evaluate the return on capital employed or operating assets within a company.
Examples of investment ratios include the price-to-earnings (P/E) ratio, return on equity (ROE), return on investment (ROI), and dividend yield.
Investment ratios provide investors with a comprehensive view of a company's performance and potential for success. They can be used to compare companies within an industry and evaluate stocks.
Investment ratios are calculated by dividing one variable by another. For example, the P/E ratio is calculated by dividing the current stock price by earnings per share.
While investment ratios are useful tools, they should not be the sole basis for investment decisions. They should be used in combination with other types of analysis and company-specific information. Additionally, company executives can manipulate accounting practices to make ratios appear more favourable.