Health savings accounts (HSAs) are a great way to save for future medical expenses and offer triple tax benefits. Contributions reduce your taxable income, the money grows tax-free, and withdrawals for qualified medical expenses aren't taxed either. You can invest HSA funds in stocks, bonds, mutual funds, and other assets, but there are some pros and cons to consider.
The advantages of investing HSA funds include the potential for long-term growth, tax-free investment earnings, and the ability to supplement your retirement funds. However, there is a risk of losing money due to market volatility, and you may have to pay transaction and management fees. Additionally, investing usually requires a long-term commitment, so your funds may be inaccessible if you need them for a medical emergency.
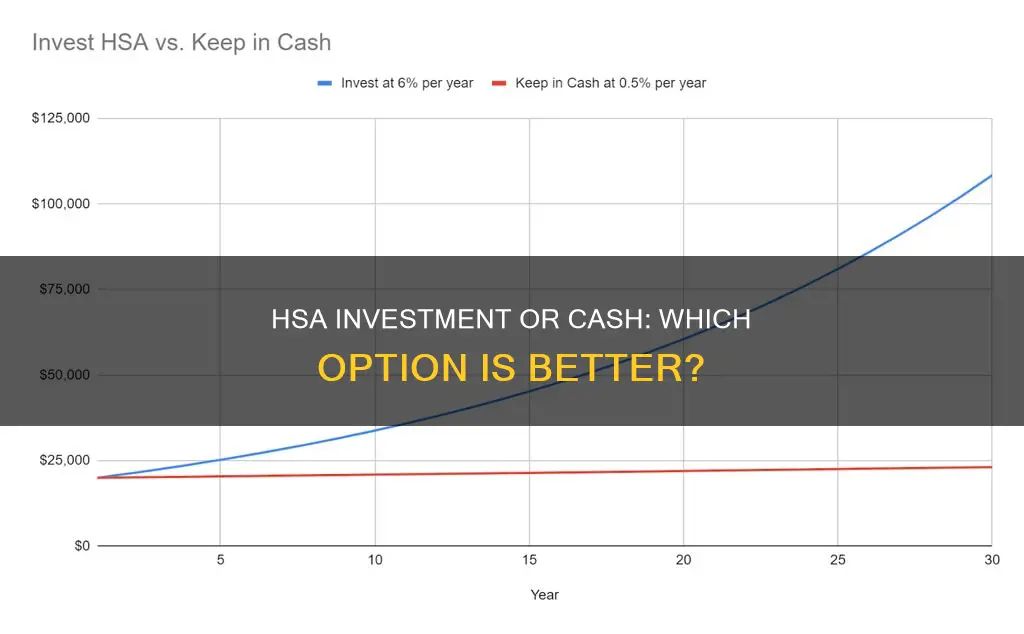
Before deciding whether to invest your HSA or leave it as cash, consider your financial goals, risk tolerance, and potential future medical needs. If you have a high-deductible health plan and expect significant medical expenses in the near future, it may be best to keep your HSA as cash to ensure you can cover those costs. On the other hand, if you're using your HSA primarily for retirement and can cover medical expenses with other funds, investing could be a good option to boost your savings.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Tax advantages | No federal income tax on contributions; tax-free growth and withdrawals for qualified medical expenses; tax-free withdrawals for non-medical expenses after age 65 |
| Investment options | Stocks, bonds, mutual funds, exchange-traded funds (ETFs), certificates of deposit (CDs), money market funds, dividend funds, individual stocks |
| Pros | Opportunity to grow savings; tax advantages; supplement to retirement funds |
| Cons | Risk of losing money; potential fees; potential inaccessibility of funds |
What You'll Learn

Investing HSA funds can be a good way to supplement retirement savings
Investing your Health Savings Account (HSA) funds can be a good way to supplement your retirement savings. Here are some reasons why:
Tax Benefits
HSAs offer a triple tax advantage. Firstly, you don't pay federal income tax on contributions. Secondly, you won't be taxed on withdrawals for qualified medical expenses. Finally, your earnings from investments won't be taxed. This means that you can grow your money tax-free, and your funds can compound more easily.
Retirement Supplement
If you've maxed out your other tax-protected retirement savings account contributions, such as IRAs and 401(k)s, investing your HSA funds can be a great way to boost your overall retirement savings. Once you're older than 65, you can make HSA withdrawals for non-medical expenses without penalty.
Long-Term Growth
Investing your HSA funds can offer the opportunity for long-term growth. You can invest in assets like stocks, bonds, and mutual funds, which could earn returns that surpass inflation and help your funds grow.
Diversification
Investing your HSA funds can provide diversification to your overall retirement strategy. You can choose from a range of investment options, including stocks, bonds, mutual funds, exchange-traded funds (ETFs), and money market funds, depending on your goals and risk tolerance.
However, it's important to note that investing your HSA funds may not be suitable for everyone. There are some potential downsides and restrictions to consider:
- Minimum Balance Requirements: Some HSA administrators require a minimum balance in your account before allowing you to invest.
- Risk of Loss: As with any investment, there is a risk of losing money due to market volatility and economic downturns.
- Fees: Your HSA provider may charge transaction, management, and account fees for investing your funds, which could impact your overall returns.
- Limited Investment Options: Some HSAs may not offer the investment options you prefer, or they may charge higher fees than you'd like.
- Inaccessibility: Investing your HSA funds typically requires a long-term commitment, so if you need money for immediate medical expenses, investing may not be ideal.
- High-Deductible Health Plan Requirement: HSAs must be tied to a high-deductible health plan, which may not be suitable for those with high medical expenses.
Therefore, when deciding whether to invest your HSA funds, carefully consider your unique financial goals, risk tolerance, and circumstances. Both keeping your funds in cash and investing them have their advantages and disadvantages. Weigh the risks against the rewards to determine the best decision for you.
Selling Investments on Cash App: A Step-by-Step Guide
You may want to see also

You can invest HSA funds in stocks, bonds, mutual funds, and more
You can invest your HSA funds in stocks, bonds, mutual funds, and more. However, some HSA providers may not offer these options, so it is important to check with your HSA provider or administrator to confirm the investment choices available to you. Here are some of the common investment options:
- Stocks: When you invest in stocks, you own shares of an individual company, and your savings can increase as the company grows. However, investing in individual stocks is a risky approach as it lacks diversification.
- Mutual Funds: Investing in mutual funds is a great way to diversify your portfolio and potentially increase your returns while minimising your risk.
- Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs): ETFs offer diversification across a basket of stocks or other investments, and they typically have low annual fees. Some HSAs allow ETFs to be purchased with no commissions.
- Bonds: Bonds are funds issued by corporations or governments that aim to generate income through interest payments. They can be less risky and less volatile than other investment options.
- Money Market Funds: These are low-risk, short-term securities, such as commercial paper and treasury bills, that offer liquidity, stability, and returns.
- Certificates of Deposit (CDs): CDs are time deposits with maturity dates and fixed interest rates, providing stability, but they may have lower returns than other options.
When deciding whether to invest your HSA funds, it is important to consider the pros and cons. By investing, you can grow your savings over the long term and take advantage of tax-free investment earnings. Additionally, investing in an HSA can supplement your retirement funds, especially if you have reached the contribution limit on other retirement accounts. However, there are risks to investing, including the possibility of losing money due to market volatility and paying fees associated with investing. Additionally, investing tends to be a long-term commitment, so your funds may not be easily accessible if you need them for medical expenses.
Understanding Cash Flows: Notes Receivable and Operating Cash
You may want to see also

HSA funds offer a triple tax advantage
Health savings accounts (HSAs) offer a triple tax advantage, which makes them attractive savings options. Firstly, contributions to HSAs are not subject to federal income tax. This means that you don't pay tax on the money you put into your HSA. Secondly, any earnings on the account remain tax-free as long as the money is used for qualified medical expenses. This means that the money can grow without being subject to tax, and you can benefit from compound interest. Finally, the money can be withdrawn tax-free at any time to pay for qualified medical expenses. This means that you don't pay tax on the money when you take it out of the HSA.
In addition to the triple tax advantage, HSAs offer other benefits. For example, the money in an HSA can be used to pay for a wide range of qualified medical expenses, including deductibles, co-insurance, co-pays, mental health services, eye care, and dental expenses. HSAs can also be used to invest in a variety of stocks, bonds, and mutual funds, allowing your savings to grow faster. HSAs are also flexible, allowing you to choose how much money to contribute and whether to invest your savings.
However, there are also some downsides to consider. HSAs must be tied to a high-deductible health plan, which may not be suitable for those with high medical expenses. Additionally, there may be minimum balance requirements or high fees associated with HSAs. It's important to carefully consider your unique financial goals and circumstances before deciding whether to invest your HSA funds.
Understanding Capex and Cash Flow: Are They Synonymous?
You may want to see also

You can use HSA funds to cover qualifying medical costs at any age
A Health Savings Account (HSA) is a tax-advantaged account that allows you to set aside money on a pre-tax basis to pay for qualified medical expenses. This includes deductibles, copayments, coinsurance, and some other expenses. HSA funds can be used at any age to cover these qualifying medical costs, providing flexibility and discretion over how you use your healthcare dollars.
One of the key advantages of an HSA is that it offers a triple tax benefit. Firstly, contributions to an HSA are tax-deductible, reducing your taxable income. Secondly, any earnings on the account, such as interest or investment returns, remain tax-free as long as the money is used for qualified medical expenses. Finally, the money can be withdrawn tax-free at any time to pay for these expenses. This means that you can use your HSA funds to cover medical costs without incurring any additional tax burden.
It is important to note that if you spend your HSA money on non-qualified expenses, you may be subject to a penalty and taxes on the withdrawal. However, once you reach the age of 65, the rules change slightly. At this age, you can use the money in your HSA for any reason without incurring a penalty, although you will be required to pay ordinary income tax on non-qualified withdrawals.
In summary, an HSA provides a valuable way to save for and cover medical expenses at any age, while also offering tax advantages that can help your savings grow over time.
Maximizing Your Cash Inheritance: Smart Investment Strategies
You may want to see also

HSAs must be tied to a high-deductible health plan
A Health Savings Account (HSA) is a tax-advantaged account that allows you to pay current medical bills and save for future medical expenses. It can also be used to invest in a variety of stocks, bonds, and mutual funds. HSAs are only available to those with a high-deductible health insurance plan. In 2024, the minimum deductible for an individual is $1,600, while for a family, it is $3,200.
HSAs have a triple tax benefit:
- Contributions are tax-deductible.
- Withdrawals for qualified medical expenses are not taxed.
- Earnings on the account remain tax-free as long as the money is used for qualified medical expenses.
If you withdraw HSA funds for non-qualified expenses, you will be charged a 20% bonus penalty in addition to income taxes on the withdrawal. However, once you reach age 65, the bonus penalty disappears, and you can use the funds for any purpose, but you will be required to pay ordinary income tax on the withdrawal.
Some HSAs require a minimum cash balance before allowing risk investments, and some may charge transaction, management, and account fees for investing your funds.
If you have a high-deductible health plan and can afford to put money into an HSA without touching it for several years, it can be an excellent way to save for future medical expenses and supplement your retirement funds. However, if you have high medical expenses, a high-deductible plan and HSA may not be suitable, as you will need to spend significant amounts from your pocket on deductibles before your health insurance reimburses you.
Understanding Investment Impacts on Cash Flow Statements
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Investing your HSA funds can be a great way to supplement your retirement savings. You can gain tax advantages, grow your savings, and even use your HSA funds to cover qualifying medical costs at any age. Once you're older than 65, you can make HSA withdrawals for non-medical expenses without paying a penalty.
Yes, there are some potential downsides to investing your HSA funds. You may lose money due to market volatility or economic downturns, and you may have to pay fees for investing your funds. Your funds may also be inaccessible or difficult to access in the short term, as investing typically means a long-term commitment.
Depending on your HSA provider, you may be able to invest in stocks, bonds, mutual funds, money market funds, or certificates of deposit.
This will depend on your unique circumstances, including your risk tolerance and potential future medical needs. If you're using your HSA mainly as a retirement account, you may opt for high-return investments. If you have a lower risk tolerance or expect to need money for future medical expenses, you may want to focus on lower-risk investments such as short-term bond funds or money market funds.







