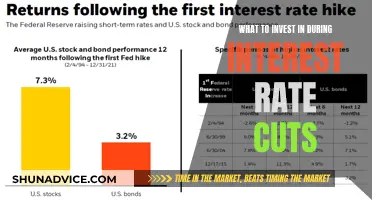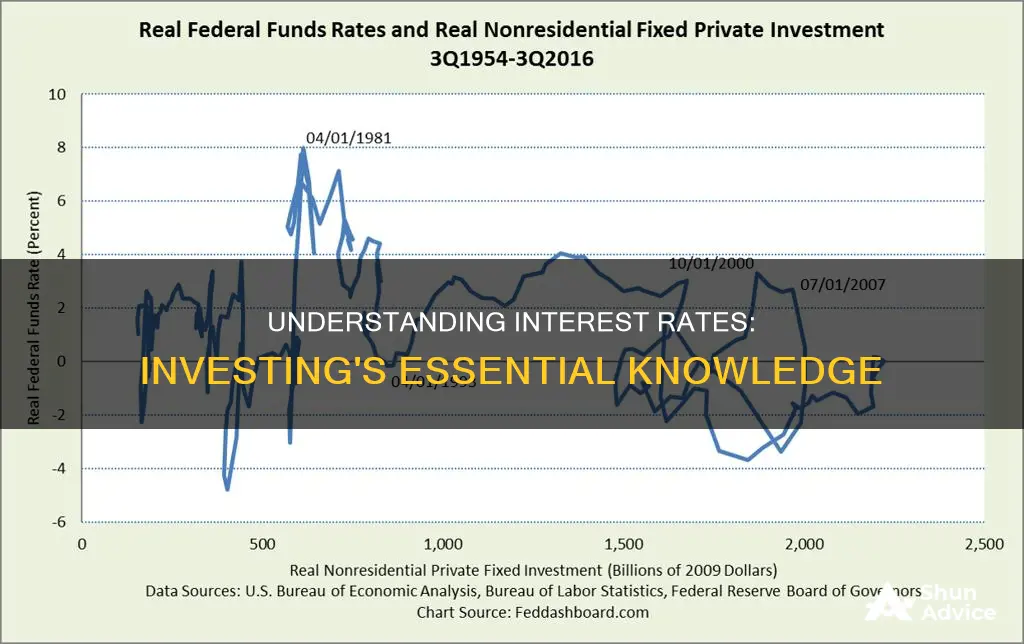
Interest rates play a key role in investment decisions. In simple terms, if the real interest rate increases, firms will demand less investment. Conversely, if the real interest rate decreases, firms will demand more investment. Investment is the allocation of funds by firms towards something they expect will generate future economic benefits, such as buying capital goods, machinery, equipment, or stockpiling inventory.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Effect of real interest rate increase | Firms will demand less investment |
| Effect of real interest rate decrease | Firms will demand more investment |
| Volatility | High |
| Factors affecting investment | Corporate taxes, predictions about the future |
What You'll Learn

The relationship between real interest rates and investment
Interest rates are a key consideration when it comes to investing. In simple terms, the relationship between real interest rates and investment is inverse: if real interest rates increase, firms will demand less investment, and if real interest rates decrease, firms will demand more investment.
This is because firms will invest up to the point that they consider it profitable. When considering an investment project, firms are required to make predictions about the future, and any fluctuation in their opinion on what the future might hold will affect their choices. For example, according to the theory of rational expectations, borrowers and lenders form an expectation of inflation in the future, which will impact their investment decisions.
Investment is generally very volatile, and there are good reasons for this. When undertaking an investment, firms make a marginal benefit and marginal cost comparison. Investment is also affected by corporate taxes, as firms make their calculations for net or after-tax profits when making investment decisions.
Mastering the Art of Time and Compound Interest
You may want to see also

The effect of interest rates on investment
Interest rates are a key consideration when it comes to investing. In simple terms, there is an inverse relationship between the real interest rate and investment. This means that if the real interest rate increases, firms will demand less investment. Conversely, if the real interest rate decreases, firms will demand more investment.
Firms will invest up to the point that they consider it profitable. When considering an investment project, firms are required to make predictions about the future, and any fluctuation in their opinion on what the future might hold will affect their choices. Investment is generally very volatile, and there are good reasons for this. For example, corporate taxes can affect investment decisions, as firms make their calculations for net or after-tax profits.
The Fisher equation applies both ex ante and ex post. Ex ante, the rates are projected rates, whereas ex post, the rates are historical. There is a market for investments, including the money market, bond market, stock market, and currency market as well as retail banking.
According to the theory of rational expectations, borrowers and lenders form an expectation of inflation in the future, which can also affect investment decisions.
How Interest Rates Affect Investment Decisions
You may want to see also

The average interest rate on investments
Interest rates and investment have an inverse relationship. If the real interest rate increases, firms will demand less investment, and if the real interest rate decreases, firms will demand more investment.
The type of savings account you have has a big impact on the amount of interest you'll earn. The amount of interest you can earn from a savings account depends on the annual percentage rate (APY). This is a measure of your total earnings after one year when considering the base interest rate and how often interest compounds.
Understanding Long-Term Investment Interest Rates
You may want to see also

The marginal benefit and marginal cost comparison
When considering an investment project, firms are required to make predictions about the future, and any fluctuation in their opinion on what the future might hold will affect their choices. Investment is generally very volatile, and there are good reasons why.
Firms will invest up to the point that it considers it profitable. This is because of the marginal benefit and marginal cost comparison that each firm is making when undertaking an investment.
In economics, investment is the allocation of funds by firms towards buying capital goods, machinery, equipment, or inventory. All these are expected to increase the firm's profits in the future. Investment is the allocation of funds by firms towards something they expect will generate future economic benefits.
If the real interest rate increases, firms will demand less investment. Conversely, if the real interest rate decreases, firms will demand more investment, other things being equal.
Interest Rate Changes: Impact on Valuations, Investments, Mortgages
You may want to see also

The theory of rational expectations
Interest rates are an important consideration when investing. In simple terms, the relationship between the real interest rate and investment is inverse: when the real interest rate increases, firms will demand less investment, and when it decreases, firms will demand more investment. This is because of the marginal benefit and marginal cost comparison that each firm makes when undertaking an investment.
Firms will invest up to the point that they consider it profitable. When considering an investment project, firms are required to make predictions about the future, and any fluctuation in their opinion on what the future might hold will affect their choices. Investment is generally affected by corporate taxes, as firms make their calculations for net or after-tax profits when making investment decisions.
Interest Rates: Impact on Consumption, Investment, and Exports
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
If the real interest rate increases, firms will demand less investment. Conversely, if the real interest rate decreases, firms will demand more investment.
Yes, investments are generally very volatile and can be affected by interest rates.
Corporate taxes affect investment because firms make their calculations for net or after-tax profits when making investment decisions.
The Fisher equation applies to interest rates both ex ante and ex post. Ex ante, the rates are projected rates, whereas ex post, the rates are historical.
According to the theory of rational expectations, borrowers and lenders form an expectation of inflation in the future.